
Metallographic Video Clips

MATERIALS PLUS Decarburization VIDEO'S
Decarburization is the loss of carbon at the metals surface due to chemical reaction(s) with the contacting media. Decarburization can over time significantly change the surface properties of the metal. ASTM E1077 (Standard Test Methods for Estimating the Depth of Decarburization of Steel Specimens) provides the guidelines for estimating the average or greatest depth of decarburization in hardened or non-hardened steel products. Metallographic analysis of a properly polished and etched sample is considered an acceptable technique for determining decarburization for heated-treated, spherodize-annealed, cold-worked, as-hot rolled, as-forged, annealed, or normalized steel specimens. The depth of decarburization can be determined by the observed changes in the microstructural cross-section due to changes in the carbon content.ASTM defines the following terms:
- Average depth of decarburization – the mean value of 5 or more measurements of the total depth of decarburization.
- Average free-ferrite depth – the mean value of 5 or more measurements of the depth of complete decarburization
- Complete decarburization – loss of carbon content at the surface of a steel specimen to a level below the solubility limit of carbon in ferrite so that only ferrite is present.
- Partial decarburization – loss of carbon content at the surface of a steel specimen to a level less than the bulk carbon content of the unaffected interior by greater then the room temperature solubility limit of carbon in ferrite. The partial decarburization zone would contain both ferrite and pearlite.
- Total depth of decarburization – the perpendicular distance from the specimen surface to that location in the interior where the bulk carbon content is reached; that is, the sum of the depths of complete and partial decarburization.
- For heat-treated specimens, the presence of non-martensitic structures in the partially decarburized zone is used to estimate the total depth of decarburization.
- Maximum depth of decarburization – the largest measured value of the total depth of decarburization.
MATERIALS PLUS Decarburization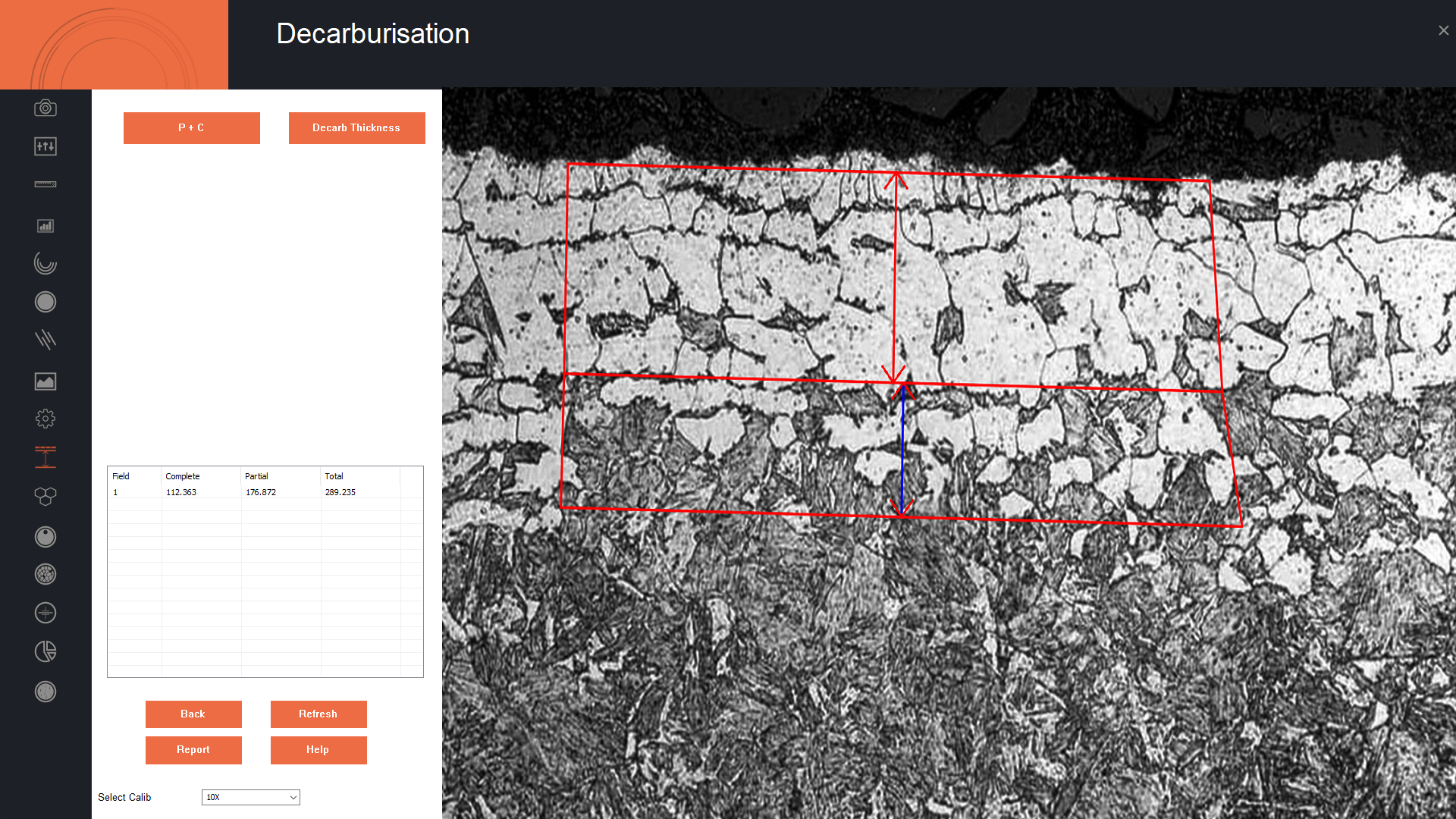
|

 MATERIALS PLUS Decarburization Specifications
MATERIALS PLUS Decarburization Specifications
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Decarburization |  |
| Testing Standard(s) | ASTM E562 & E1245 |
| Example Procedure |